The struct type is suitable for representing lightweight. A struct would be less expensive. It is declared as
public struct Rect
{
public double height;
public double width;
public Rect(double d1, double d2)
{
height = d1;
width = d2;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "(" + height +"," + width + ")";
}
}
It is used as
Rect r1 ;
r1.height = 10;
r1.width = 20;
Console.WriteLine(r1.ToString());
Rect r2 = new Rect(12, 23);
Console.WriteLine(r2.ToString());
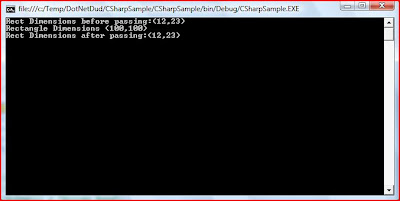
- Structs are value types and classes are reference types. That is when you pass the struct to a method you pass the value and not the reference.
Rect r2 = new Rect(12, 23);
Console.WriteLine("Rect Dimensions before passing:" + r2.ToString());
change_the_struct(r2);
Console.WriteLine("Rect Dimensions after passing:" + r2.ToString());
private static void change_the_struct(Rect Rectangle1)
{
Rectangle1.height = 100;
Rectangle1.width = 100;
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle Dimensions " + Rectangle1.ToString());
}
It will give the following output, which shows the struct is passed by value.
- Unlike classes, structs can be instantiated without using a new operator. Static classes are an exception ()
Rect r1 ;
r1.height = 10;
r1.width = 20;
Console.WriteLine(r1.ToString());
- Structs can declare constructors, but they must take parameters.
public struct Rect
{
public double height;
public double width;
public Rect(double d1, double d2)
{
height = d1;
width = d2;
}
}
- A struct cannot inherit from another struct or class, and it cannot be the base of a class. All structs inherit directly from System.ValueType, which inherits from System.Object.
- Structs cannot have destructors, whereas classes can
See also :
How to Create Interfaces in .NET / Interfaces in .NET
How to Create Classes in C#
Properties in .NET / Get and Set Methods in .NET































No comments:
Post a Comment